Dealing with Hip Pain
Understanding Common Causes of Hip Pain
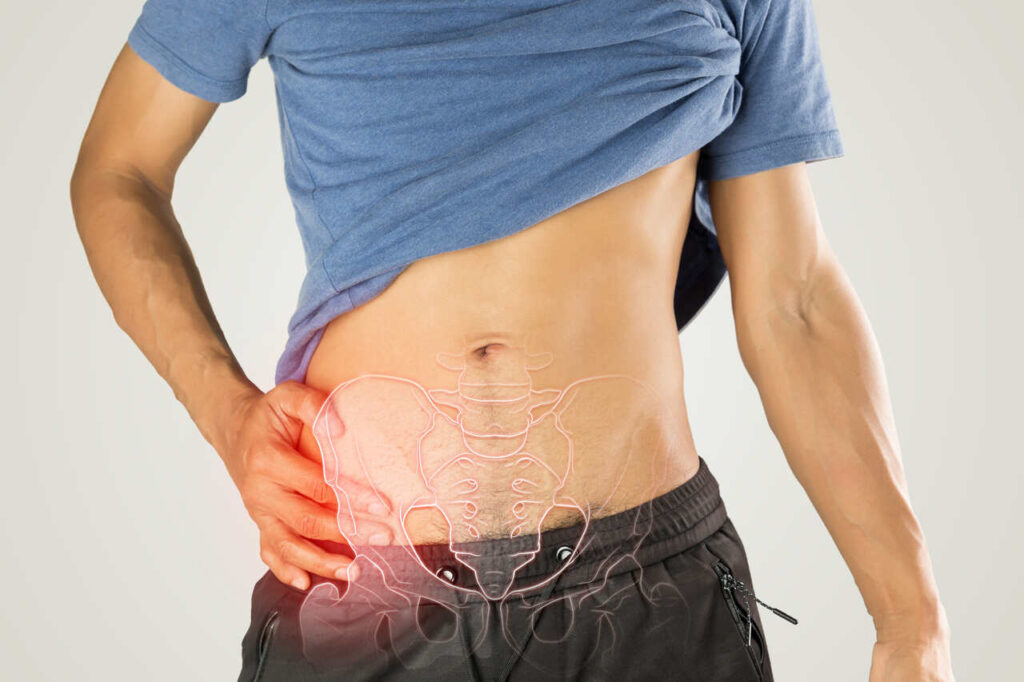
Hip pain can stem from various sources, and understanding the root cause is crucial for effective treatment. Several common causes include:
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis can lead to hip discomfort and stiffness.
- Injuries: Fractures, sprains, and dislocations can severely impact the hip joint.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joints, often leads to pain.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons, commonly due to overuse.
- Muscle Strain: Overstretching or tearing of muscles around the hip.
- Labral Tear: Damage to the ring of cartilage (labrum) around the hip socket.
Below is a table summarizing the common causes of hip pain and their symptoms:
| Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Arthritis | Pain, stiffness, reduced range of motion |
| Injuries | Sharp pain, swelling, bruising |
| Bursitis | Pain, swelling, tenderness |
| Tendonitis | Pain, especially during movement |
| Muscle Strain | Pain, weakness, muscle spasms |
| Labral Tear | Locking, clicking, instability, pain |
Importance of Seeking Physiotherapy
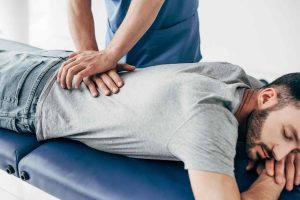
Physiotherapy plays a pivotal role in managing and alleviating hip pain. Seeing a qualified physiotherapist can help you identify the underlying causes of your discomfort and create a tailored treatment plan. Here are key reasons why seeking physiotherapy is crucial:
- Pain Relief: Targeted exercises and manual therapy can help reduce pain and improve mobility.
- Improved Functionality: Strengthening and stretching exercises can restore and enhance hip function.
- Prevent Further Injury: Proper guidance and treatment can prevent recurring issues or additional damage.
- Personalized Care: A physiotherapist can develop a specific program to address your unique needs and goals.
By opting for physiotherapy, you take a proactive step towards better hip health and overall well-being. Discover more about physiotherapy treatments available for hip pain.
For further assistance, you can locate a physiotherapy clinic near you or learn more about physiotherapy exercises beneficial for hip pain.
Physiotherapy Assessment
The first step in addressing your hip pain through physiotherapy is a comprehensive assessment. This involves both an initial consultation and a physical examination to establish a clear understanding of your condition and to design an appropriate treatment plan.
Initial Consultation
During the initial consultation, your physiotherapist will gather extensive information about your hip pain. They will ask questions regarding your medical history, the onset and duration of your pain, its severity, and any activities that aggravate or alleviate it. This detailed discussion allows the physiotherapist to identify potential causes and understand how the pain impacts your daily life.
| Information Collected | Importance |
|---|---|
| Medical History | Identifies past injuries or conditions |
| Pain Onset & Duration | Determines whether the issue is acute or chronic |
| Pain Severity | Assesses the intensity of discomfort |
| Activity Triggers | Identifies movements that exacerbate or relieve pain |
The consultation may also include questions about your lifestyle, work environment, and stress levels. This holistic approach ensures that all contributing factors to your hip pain are considered.
Physical Examination
Following the consultation, a physical examination is essential to assess the current state of your hip and related structures. This examination involves several components:
- Visual Inspection: Observing your hip alignment, posture, and any visible abnormalities.
- Palpation: Feeling the hip area to identify tender spots, swelling, or muscle tightness.
- Range of Motion Tests: Measuring the flexibility and movement of your hip joint to determine any limitations or restrictions.
- Strength Tests: Evaluating the strength of muscles around the hip to identify imbalances or weaknesses.
- Functional Tests: Assessing your ability to perform specific movements or activities that may trigger pain.
The results of these tests help pinpoint the exact nature of your hip pain and its impact on your functionality. For more detailed information on specific tests used during the assessment, refer to our article on physiotherapy for hip pain.
| Test Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Visual Inspection | Identifies visible signs of pain or injury |
| Palpation | Detects tender spots, swelling, and tightness |
| Range of Motion Tests | Assesses flexibility and joint movement |
| Strength Tests | Evaluates muscle strength and imbalances |
| Functional Tests | Observes movement patterns and triggers |
By combining the insights from the initial consultation and physical examination, your physiotherapist can develop a tailored treatment plan. This may include various physiotherapy treatments, therapeutic exercises, and lifestyle modifications to help reduce your hip pain and improve your overall function.
Physiotherapy Treatments
In addressing hip pain, there are several physiotherapy approaches that can provide relief and promote healing. The treatments include manual therapy techniques, therapeutic exercises, and the use of various modalities and tools.
Manual Therapy Techniques
Manual therapy involves hands-on techniques to manipulate and mobilize the affected area. These techniques aim to improve joint function, reduce pain, and increase mobility. Here are some common manual therapy techniques used in physiotherapy for hip pain:
- Joint Mobilization: Gentle, controlled movements of the hip joint to improve its range of motion.
- Soft Tissue Mobilization: Techniques such as massage to alleviate muscle tension and enhance blood flow.
- Myofascial Release: Applying pressure to the connective tissues around muscles to relieve tightness and pain.
Therapeutic Exercises
Therapeutic exercises play a vital role in strengthening the muscles around the hip joint, enhancing flexibility, and reducing pain. A physiotherapist will tailor an exercise program to your specific condition, focusing on areas that need improvement. Common therapeutic exercises include:
- Stretching Exercises: These exercises help improve the flexibility of the hip muscles. Examples include hamstring stretches, hip flexor stretches, and piriformis stretches.
- Strengthening Exercises: Building muscle strength around the hip can provide better support to the joint. Exercises like bridges, leg lifts, and squats are commonly used.
- Balance and Stability Exercises: These exercises focus on improving your balance and coordination, which can help prevent future injuries. Examples include single-leg stands and stability ball exercises.
For more physiotherapy exercises, visit our detailed guide.
| Exercise Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Stretching | Hamstring stretches, hip flexor stretches |
| Strengthening | Bridges, leg lifts, squats |
| Balance & Stability | Single-leg stands, stability ball exercises |
Modalities and Tools Used in Treatment
Physiotherapy also employs various modalities and tools to manage pain, promote healing, and improve function. These modalities might include:
- Electrotherapy: Uses electrical currents to reduce pain and inflammation. Techniques such as TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation) and ultrasound therapy are common.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: Application of heat packs to relax muscles or ice packs to reduce inflammation and numb the painful area.
- Hydrotherapy: Exercises performed in water to reduce the stress on the hip joint while boosting strength and flexibility.
- Dry Needling: Inserting fine needles into specific trigger points to release muscle tension and pain.
Different modalities offer unique benefits depending on the condition and severity of your hip pain. Your physiotherapist can guide you through the best options suited for your needs.
Lifestyle Recommendations
Incorporating lifestyle changes can significantly contribute to managing and preventing hip pain. Here, we’ll discuss ergonomic adjustments and activity modifications that can help you maintain a pain-free lifestyle.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ergonomic adjustments involve modifying your environment to support your body’s natural alignment and reduce strain on your hips. These changes are especially important if you spend long hours sitting or standing.
-
Workstation Setup: Ensure your chair and desk are at appropriate heights. Your knees should be at a right angle with your feet flat on the floor. Use a chair that supports your lower back.
-
Standing Posture: Maintain a straight posture with shoulders back and weight evenly distributed on both feet. Avoid locking your knees.
-
Sleeping Position: Sleep on your side with a pillow between your knees to keep your hips aligned.
Recommended Ergonomic Adjustments
| Area | Adjustments |
|---|---|
| Sitting | Chair with lumbar support, feet flat on the floor |
| Standing | Weight evenly distributed, avoid locking knees |
| Sleeping | Side sleeping with pillow between knees |
For more on ergonomic adjustments across different environments, please refer to our detailed article on physiotherapy near me.
Activity Modification
Activity modification involves altering your routine to minimize activities that exacerbate hip pain while incorporating beneficial ones.
-
Low-Impact Exercises: Engage in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling. These activities provide a good workout without putting excessive stress on your hips.
-
Avoid Prolonged Sitting: Take breaks to stand and stretch every hour if you have a sedentary job.
-
Proper Warm-Up: Always warm up before any physical activity. Gentle stretching can prepare your hip muscles for activity.
Recommended Activity Modifications
| Activity | Modification |
|---|---|
| Exercise | Swim, cycle, or walk instead of running |
| Sitting | Stand and stretch every hour |
| Warm-Up | Gentle stretching before physical activities |
For more detailed exercise guides and modifications, check out our section on physiotherapy exercises.
Incorporating these ergonomic and activity modifications can aid in reducing hip pain. Remember, consulting with a physiotherapist for personalized advice can provide more targeted solutions. For further reading, explore our articles on physiotherapy for chronic pain and physiotherapy for arthritis.
Preventing Future Hip Pain
Preventing future hip pain is essential for maintaining mobility and quality of life. Here, we’ll discuss ways to achieve this through home exercise programs and long-term management strategies.
Home Exercise Programs
A well-structured home exercise program can help strengthen the muscles around your hips, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. It’s important to consult with a physiotherapist to tailor an exercise routine suited for your condition. Here are some common exercises that might be included:
| Exercise | Purpose | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Hip Bridges | Strengthen glutes and lower back | 2-3 times a week |
| Clamshells | Strengthen hip abductors | 2-3 times a week |
| Leg Raises | Strengthen hip flexors | Daily |
| Stretching | Improve flexibility | Daily |
For more examples of exercises, check out our detailed guide on physiotherapy exercises.
Long-Term Management Strategies
Achieving long-term hip health requires consistent effort and attention to several factors. Here are some strategies to help you manage and prevent hip pain in the long run:
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on the hip joints.
- Posture Improvement: Proper posture minimizes undue strain on your hips.
- Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate low-impact activities like swimming or cycling.
- Ergonomic Adjustments: Make sure your workplace and home setups are hip-friendly.
- Periodic Physiotherapy Check-ups: Regular visits to a physiotherapy clinic are beneficial for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments.
These long-term strategies can play a significant role in keeping hip pain at bay, ensuring that you stay active and pain-free. By following the given advice and staying committed, you can effectively manage your hip health and prevent future pain. For more information, you can explore our article on physiotherapy for hip pain.