Understanding Psychotherapy for ADHD
What is ADHD and How Does it Impact Us?
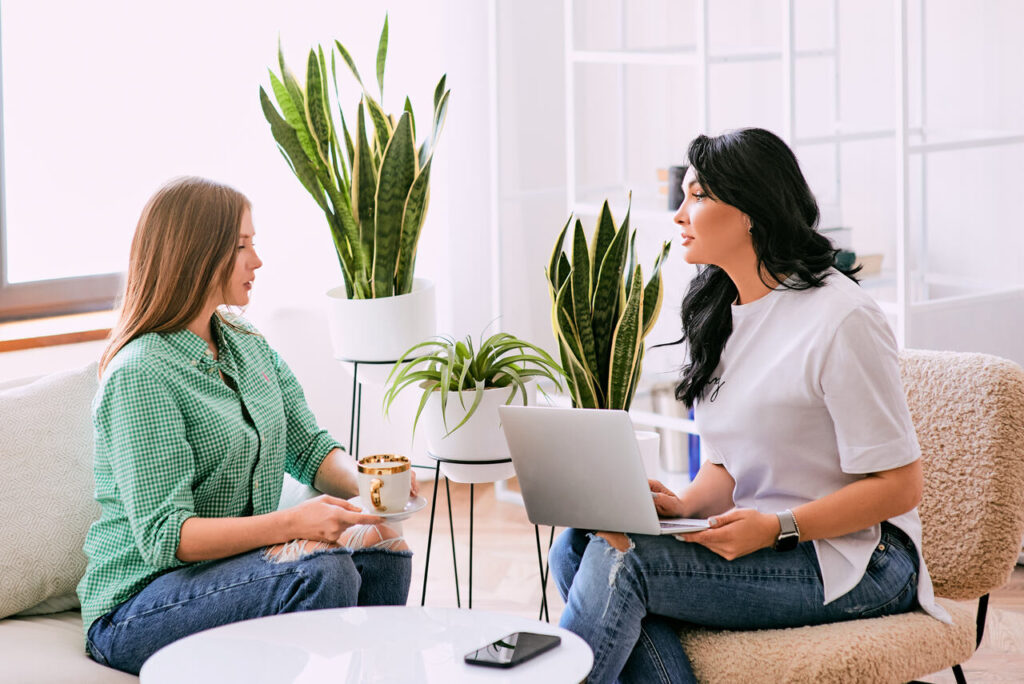
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms can vary in severity and often impact various aspects of daily life, including academic performance, occupational responsibilities, and interpersonal relationships.
ADHD can make it challenging for us to stay focused, follow through with tasks, and regulate our emotions. The symptoms can lead to difficulties in organizational skills, time management, and maintaining attention on tasks that require sustained mental effort. Understanding ADHD is crucial to recognizing the potential impact it has on our lives and seeking effective treatments.
The Role of Psychotherapy in Managing ADHD
Psychotherapy, also known as talk therapy or counseling, plays a pivotal role in managing ADHD. Psychotherapy for ADHD helps us to develop strategies and skills necessary to cope with our symptoms. Through various therapeutic approaches, we can learn to improve our focus, enhance our emotional regulation, and foster better coping mechanisms.
One of the primary forms of psychotherapy used for ADHD is Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT). CBT helps us identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors that may contribute to our ADHD symptoms. By focusing on problem-solving and skill-building, CBT equips us with tools to manage our attention and hyperactivity.
Another beneficial approach is Mindfulness-Based Therapies, which teach us mindfulness techniques to improve our attention and reduce impulsivity. These therapies promote awareness of the present moment and help us manage our symptoms more effectively.
| Type of Therapy | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy | Improves focus, reduces negative thought patterns |
| Mindfulness-Based Therapies | Enhances attention, reduces impulsivity |
| Interpersonal Therapy | Improves communication, fosters better relationships |
Psychotherapy for ADHD is most effective when incorporated into a comprehensive treatment plan that may also include medication and lifestyle changes. Collaborating with a qualified therapist can provide us with a supportive environment to explore our challenges and work towards better focus and clarity. For more information on psychotherapy and its applications, you can explore our articles on psychotherapy for anxiety and psychotherapy for depression.
In sum, psychotherapy offers valuable tools and strategies for managing ADHD symptoms and improving our overall quality of life. Whether it’s through CBT, mindfulness, or other therapeutic approaches, psychotherapy can be a transformative part of our journey towards better focus and clarity.
Types of Psychotherapy
Exploring the various types of psychotherapy available for ADHD can help us determine the best approach to managing our symptoms and improving our overall well-being. By understanding the different therapy options, we can make informed decisions about incorporating them into our treatment plans.
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is one of the most widely used forms of psychotherapy for ADHD. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns and behaviors that can contribute to our difficulties with attention and focus. Through this therapy, we learn to develop healthier ways of thinking and coping strategies.
CBT often involves:
- Identifying negative thoughts
- Replacing negative thoughts with positive ones
- Developing problem-solving skills
- Setting achievable goals
Approximate Success Rates for CBT in ADHD:
| Age Group | Success Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Children | 65 |
| Adolescents | 70 |
| Adults | 50 |
For those interested in CBT for other conditions, check out our article on psychotherapy for anxiety.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) is another effective form of psychotherapy for ADHD. Originally developed for borderline personality disorder, DBT has been adapted to help individuals with ADHD manage their emotions and improve their relationships. DBT combines cognitive-behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices.
Key components of DBT include:
- Mindfulness skills
- Emotion regulation
- Distress tolerance
- Interpersonal effectiveness
Individuals who practice DBT often experience improved emotional regulation and better coping mechanisms. More information on DBT for other conditions can be found in our article on psychotherapy for trauma.
Interpersonal Therapy
Interpersonal Therapy (IPT) focuses on improving our interpersonal relationships and social functioning, which can be particularly beneficial for those of us with ADHD. IPT helps us identify and address issues in our relationships that may be contributing to our ADHD symptoms.
Core aspects of IPT include:
- Identifying problematic relationships
- Improving communication skills
- Developing healthier relationship patterns
- Addressing role transitions and conflicts
IPT Success in Improving Social Functioning in ADHD:
| Symptom Area | Improvement (%) |
|---|---|
| Communication Skills | 60 |
| Relationship Satisfaction | 55 |
| Social Functioning | 65 |
For additional reading, see our article on psychotherapy for relationship issues.
Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Mindfulness-Based Therapies, such as Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) and Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR), are becoming increasingly popular for managing ADHD symptoms. These therapies emphasize mindfulness practices to help us stay present in the moment and reduce distractions.
Benefits of Mindfulness-Based Therapies include:
- Improved focus and attention
- Reduced impulsivity
- Better emotional regulation
- Enhanced overall well-being
For more information on stress management techniques, refer to our article on psychotherapy for stress management.
By exploring these various types of psychotherapy, we can find the approach that best suits our needs and helps us manage our ADHD symptoms effectively.
Benefits of Psychotherapy for ADHD
Improved Focus and Attention
One of the primary benefits of psychotherapy for ADHD is the improvement in focus and attention. Through different therapeutic approaches such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and Mindfulness-Based Therapies, we learn techniques to better manage our attention and minimize distractions. By incorporating strategies like time management and prioritization skills, psychotherapy helps us improve our efficiency in daily tasks and reduce the feelings of being overwhelmed.
| Technique | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Teaches structured problem-solving; improves focus |
| Mindfulness-Based Techniques | Enhances awareness and attention span |
Better Emotional Regulation
Psychotherapy aids in the better regulation of emotions, which is often a challenge for individuals with ADHD. By understanding our emotional responses and learning coping skills, we can respond to stress and frustration more effectively. Therapies such as Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) and Interpersonal Therapy help in recognizing and modifying our behaviors to maintain emotional stability.
| Therapy Type | Emotional Benefit |
|---|---|
| Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT) | Improves emotional regulation |
| Interpersonal Therapy | Enhances social interactions and emotional understanding |
Enhanced Coping Skills
One of the significant benefits of psychotherapy for ADHD is the development of enhanced coping skills. Through various behavioral strategies and skill-building exercises, we learn how to manage the symptoms of ADHD more effectively. These skills are crucial for dealing with the everyday challenges that come with ADHD, including time management, organization, and dealing with hyperactivity.
| Coping Mechanism | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Skill-Building Exercises | Improve daily functioning |
| Behavioral Strategies | Manage symptoms and reduce hyperactivity |
By embracing these benefits, we can experience a greater sense of clarity and control in our lives. Psychotherapy offers a pathway to better manage ADHD and achieve personal growth.
For further exploration of different therapeutic approaches, visit our articles on psychotherapy for anxiety, psychotherapy for depression, and psychotherapy for stress management.
Incorporating Psychotherapy into Treatment
Incorporating psychotherapy into our treatment for ADHD can significantly enhance our journey towards better focus and clarity. Here’s how we can seamlessly blend it into our lives.
Collaborating with a Therapist
Collaborating with a therapist is a fundamental step in our journey. Therapists help us understand our ADHD in depth and work with us to develop personalized strategies. A good rapport with our therapist fosters a safe space for open communication, which is critical in addressing our specific needs.
When searching for a therapist, we should consider their experience with ADHD and psychotherapy. We can find specialized professionals by exploring options for psychotherapy for anxiety or similar therapeutic contexts to ensure they’re well-versed in cognitive and behavioral interventions.
Setting Realistic Goals
Setting realistic goals is pivotal for our progress in therapy. ADHD can make it challenging to keep track of our tasks, and having clear, attainable targets helps us stay focused. Our therapist guides us in breaking down larger objectives into smaller, manageable steps.
We can use the following table to track our goals:
| Goal | Steps | Timeline | Progress |
|---|---|---|---|
| Improve Focus | 1. Use timers 2. Limit distractions |
1 month | In progress |
| Enhance Emotional Regulation | 1. Practice mindfulness 2. Identify triggers |
3 months | Not started |
| Build Coping Skills | 1. Attend therapy 2. Practice skills |
Ongoing | Partial |
Tracking our progress helps in evaluating the effectiveness of our goals and adjusting them as needed. This strategy is similarly applicable in contexts like psychotherapy for depression or psychotherapy for trauma.
Practicing Skills Learned in Therapy
The skills we learn in therapy become powerful tools in managing ADHD. These might include behavioral strategies, mindfulness techniques, or time management practices. Consistently applying these skills in our daily routines reinforces new habits and coping mechanisms.
We should regularly practice the following skills:
- Behavioral Strategies: Setting routines, using reminders.
- Mindfulness Techniques: Deep breathing, meditation.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks, scheduling breaks.
Practicing these skills is an ongoing process. By integrating what we learn in therapy into our daily lives, we can manage our ADHD symptoms more effectively. This approach is beneficial for various concerns, such as psychotherapy for stress management or psychotherapy for self-esteem.
Incorporating psychotherapy into our treatment plan empowers us to take control of ADHD and work towards a clearer, more focused path in life.
Psychotherapy Techniques for ADHD
Exploring various psychotherapy techniques can empower us to manage ADHD more effectively. Let’s delve into some of the key strategies that can aid in our journey to better focus and clarity.
Behavioral Strategies
Behavioral strategies are pivotal in helping us manage ADHD symptoms. These strategies focus on modifying our actions to achieve more desirable outcomes. Some common behavioral approaches include:
- Positive Reinforcement: Encouraging desirable behaviors by rewarding them.
- Routine Development: Establishing consistent daily routines to create structure.
- Time Management: Utilizing techniques such as timers and to-do lists to stay organized.
| Behavioral Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Positive Reinforcement | Rewarding desirable behaviors |
| Routine Development | Creating consistent daily routines |
| Time Management | Utilizing timers and to-do lists |
Skill Building Exercises
Skill building exercises are designed to help us enhance our abilities in areas where we might struggle due to ADHD. These exercises can include:
- Organizational Skills: Techniques to keep our environment orderly.
- Social Skills Training: Improving our interactions with others.
- Problem-Solving Skills: Strategies to address challenges more effectively.
Engaging in these exercises regularly can lead to significant improvements in our daily lives.
| Skill Area | Exercise |
|---|---|
| Organizational Skills | Decluttering and using labeled storage |
| Social Skills Training | Role-playing social scenarios |
| Problem-Solving Skills | Breaking down problems into smaller steps |
Coping Mechanisms
Coping mechanisms are essential tools that allow us to manage the emotional and psychological effects of ADHD. Employing effective coping strategies can reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Some useful coping techniques include:
- Mindfulness Practices: Engaging in mindfulness meditation to stay present.
- Stress Reduction Techniques: Practicing deep breathing and relaxation exercises.
- Support Networks: Connecting with supportive friends, family, or support groups.
| Coping Mechanism | Description |
|---|---|
| Mindfulness Practices | Engaging in mindfulness meditation |
| Stress Reduction Techniques | Practicing deep breathing and relaxation exercises |
| Support Networks | Connecting with supportive individuals |
Incorporating these psychotherapy techniques can greatly enhance our journey towards better focus and clarity in managing ADHD. For more information on related topics, explore our articles on psychotherapy for anxiety, psychotherapy for depression, and psychotherapy for trauma.
Embracing the Journey to Clarity
Celebrating Progress
In our journey through psychotherapy for ADHD, recognizing and celebrating progress is crucial. Achievement, no matter how small, bolsters motivation and reinforces positive behavior. When we recognize our strides in improved focus, better emotional regulation, and enhanced coping skills, we foster a sense of accomplishment.
Celebrations don’t have to be grand; they can be simple acknowledgments of our hard work. It’s important to keep track of our progress in order to see how far we’ve come. Here’s a simple way to monitor improvements:
| Progress Metric | Initial Assessment | Current Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Ability to Focus (Scale 1-10) | 4 | 7 |
| Emotional Regulation (Scale 1-10) | 3 | 6 |
| Use of Coping Skills (Complete Tasks per Week) | 2 | 5 |
By continuously updating this table, we can visualize the impact of our efforts and celebrate each milestone.
Continuing Self-Reflection and Growth
Our path to better focus and clarity through psychotherapy for ADHD is ongoing. Self-reflection is an essential part of understanding our thoughts and behaviors. By regularly reflecting, we can identify patterns, recognize triggers, and develop better coping strategies.
Incorporating reflection into our routine can be done through various methods, such as journaling or discussing our thoughts with a therapist. Engaging in consistent self-reflection allows us to:
- Track our emotional and cognitive improvements
- Identify areas needing further development
- Strengthen the skills learned in therapy
Here’s a journal prompt list to facilitate self-reflection:
- What achievements am I proud of this week?
- What were my challenges?
- How did I apply the skills learned in therapy?
- What can I improve moving forward?
By consistently answering these questions, we ensure our continued growth on this journey. Sites like psychotherapy for stress management and psychotherapy for burnout offer additional insights to help us manage various aspects of our mental well-being.
As we embrace our journey, celebrating progress and continuing self-reflection helps us maintain clarity and focus, ultimately leading to a healthier, more balanced life.